Neuromarketing: Where Marketing & Neuroscience Meet



In today’s world, marketing has become more complex than ever before. With the ever-increasing competition in the market, it is crucial for companies to stay ahead of the curve and understand the needs and desires of their target audience. This is where neuromarketing comes in. A field that combines the principles of marketing and neuroscience to understand consumer behaviour and decision-making processes.
It’s the study of how consumers respond to marketing stimuli at the subconscious level. It involves using techniques such as brain imaging, eye-tracking, and biometric measurements to understand how consumers react to various marketing messages and stimuli. By understanding the inner workings of the brain, marketers can create more effective and persuasive marketing campaigns. It will resonate with the correct target audience.
One of the main benefits of neuromarketing is the ability to gain insights into the subconscious mind of consumers. Traditional marketing methods rely on self-reported data from consumers, which can often be inaccurate or biased. Neuromarketing on the other hand, provides objective data on how consumers react to various marketing stimuli. This will including their emotional responses, attention levels, and decision-making processes.
Another benefit of this is the ability to create more effective marketing campaigns. By understanding the neural mechanisms that underlie consumer behaviour, marketers can create messages and campaigns that resonate with their target audience at a subconscious level. This can lead to higher engagement, increased sales, and stronger brand loyalty.
The techniques include a range of tools and methods that are used to understand the brain’s response to marketing stimuli. Some of the most used techniques include: Brain Imaging, Eye-tracking, Biometric Measurements, Surveys and questionnaires. below we dive in to each of these in more detail.
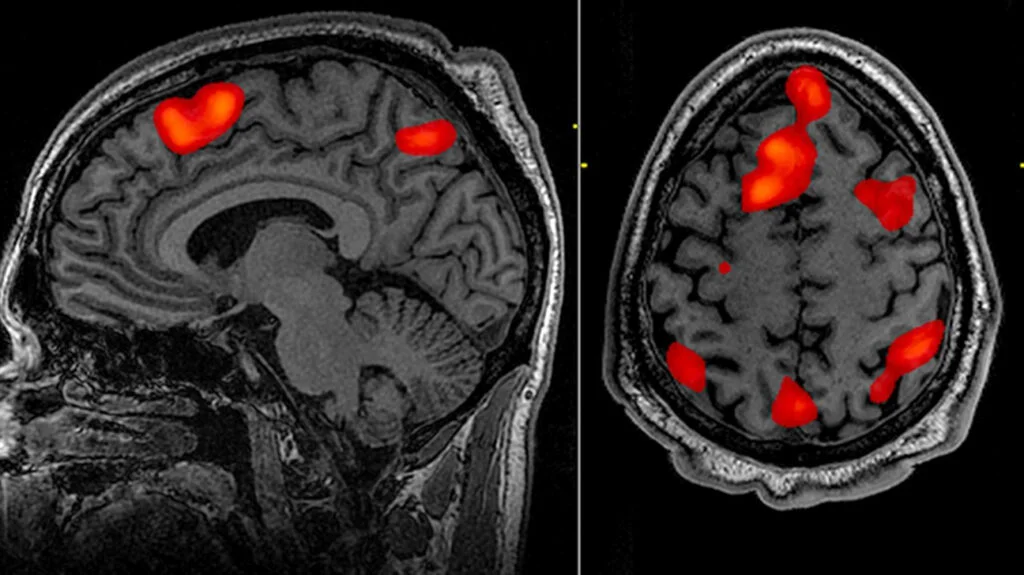

This involves using techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain activity in response to marketing stimuli.
fMRI measures changes in blood flow to different regions of the brain, allowing researchers to identify which areas are active during specific tasks or stimuli. In neuromarketing, fMRI is often used to measure consumers’ responses to marketing materials, such as advertisements or product packaging. By analysing brain activity patterns in response to these stimuli, marketers can gain insights into which elements are most engaging or persuasive to consumers.
EEG measures emotional responses to marketing materials, while fMRI and EEG have their strengths and limitations in neuromarketing research. Both techniques provide insights into neural processes underlying consumer behaviour.


Using special cameras to track the movement of a person’s eyes as they view marketing messages or products.
There are two main types of eye tracking: remote and wearable. Remote eye tracking uses cameras and infrared sensors to track the movement of the eyes from a distance, while wearable eye tracking involves placing small cameras or sensors directly on the eyes or eyeglasses.
In neuromarketing research, eye tracking can provide valuable insights into how consumers engage with different types of marketing materials. For example, by tracking where consumers look on an advertisement or website, researchers can identify which elements attract the most attention and how consumers navigate through the content.
Eye tracking can also reveal subconscious responses to marketing stimuli. For example, by measuring the amount of time consumers spend looking at certain images or text, researchers can infer which elements are most engaging or persuasive, even if the consumer is not consciously aware of it.
Overall, eye tracking provides a powerful tool for neuromarketers to understand how consumers engage with marketing materials and make decisions. By combining eye tracking with other neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI or EEG, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the neural processes underlying consumer behaviour.


Measuring physical responses such as heart rate, skin conductance, and facial expressions in response to marketing stimuli.
HRV and skin conductance are biometric measurements used in neuromarketing research to identify emotionally engaging marketing stimuli. Facial expressions are also used to identify positive or negative emotional responses. These measurements provide valuable insights into consumer behavior and can be combined with other techniques to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the processes underlying it.


Although traditional marketing research methods are often unreliable, they can still be useful when combined with neuromarketing techniques. Surveys and questionnaires can provide valuable insights into consumer attitudes and beliefs.
To better understand consumer behaviour, marketers often use surveys and questionnaires along with other neuromarketing techniques. Combining surveys with fMRI or EEG measurements provides insights into consumer behaviour.
Using surveys and questionnaires in conjunction with other neuromarketing techniques can enhance marketers’ understanding of consumer behaviour. This is useful for assessing consumers’ recall of marketing messages and gaining additional context about the stimuli presented. Employing a range of techniques can lead to more effective marketing campaigns.
Overall, surveys and questionnaires provide a valuable tool to gather information on consumers’ attitudes, beliefs, and preferences. Combining surveys with other neuromarketing techniques provides a more complete understanding of consumer behaviour.
There are several ethical implications to consider when it comes to using these techniques.
Invasion of privacy: Neuromarketing involves measuring brain activity in response to marketing stimuli, which may include sensitive personal information. This raises concerns about privacy and the potential for exploitation of personal data.
Manipulation: By tapping into consumers’ subconscious minds, neuromarketing techniques have the potential to manipulate consumers’ behaviour and decision-making. This raises concerns about this technology. Companies must prioritise ethical practices when using neuromarketing to ensure that it is in line with the best interests of their customers.
Informed consent: It is important that individuals who participate in these studies are fully informed about the nature of the research and how their data will be used. This includes ensuring that individuals have given their informed consent before participating in studies. Also, that they are aware of their right to withdraw from the study at any time.
Transparency:To ensure ethical neuromarketing practices, companies should be transparent about their methods and provide clear information to customers about research methods and data usage. This builds trust and can lead to greater brand loyalty and engagement.
In summary, businesses that utilise neuromarketing techniques must take into account the ethical implications of this technology. Moreover, it is crucial to ensure that they utilise the technology responsibly and ethically. Additionally, companies must be transparent with consumers about their methods and how their data will be used to establish trust and foster a positive relationship that can lead to greater brand loyalty and engagement.
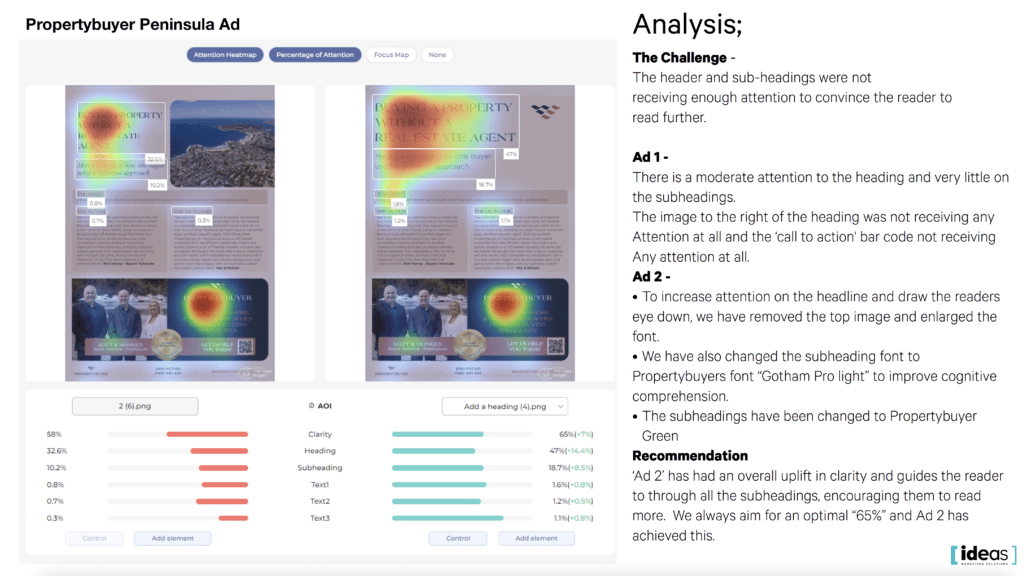
Our team used a specialised camera to track participants’ eye movements as they viewed different ads, collecting valuable data on which parts of the ad were most and least engaging. Using this data, we optimised the ad’s design and content for maximum effectiveness.
The study identified the most effective ad for Propertybuyer’s campaign,” said Scott Bouquet.





Neuromarketing combines marketing and neuroscience to gain insights into consumer behaviour and decision-making. Neuromarketing helps marketers create effective campaigns by understanding how the brain responds to marketing stimuli. As technology advances, neuromarketing’s potential applications will continue to grow, making it an essential tool for staying competitive.
As the Director of Ideas Marketing, I’ve seen firsthand how neuromarketing can impact campaign success. Using techniques like brain imaging, eye tracking, and biometric measurements, we gain deeper insights into consumer responses to our marketing.
However, it’s important to note that neuromarketing is not a magic bullet for marketing success. To fully understand consumer behaviour, companies should combine these methods with other marketing research tools, such as surveys and focus groups said Scott Bouquet.
In conclusion, I believe that neuromarketing is a powerful tool that has the potential to revolutionise the way we think about marketing. By harnessing the power of the human brain, we can create more engaging and effective marketing campaigns that truly resonate with our target audience. As the field continues to evolve, I look forward to seeing how it will continue to shape the future of marketing.
Author: Scott Bouquet


This site is not available in landscape mode,
Please turn your mobile.
Bonjour, comment pouvons-nous vous aider ?